Snake Oil
Home >
Huntress CTF > Medium Challenges
Back <> Next
One of our workstations was exhibiting strange network communications… we found this binary that looked to be the culprit. Can you find anything suspicious?
Here we are given the file ‘snake-oil’ to download and inspect.
Note: We found three ways to solve this challenge…
Method 1:
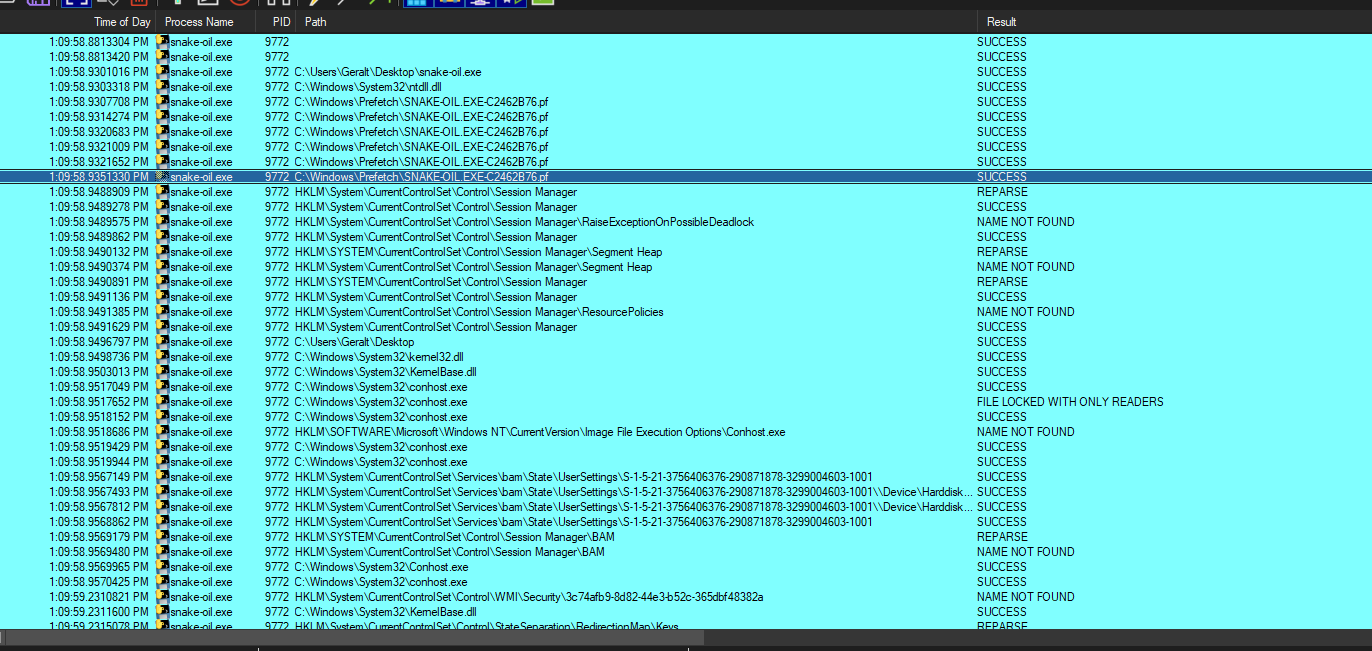
First we set a filter in Process Monitor for process name is snake_oil.exe, and ran the executable.
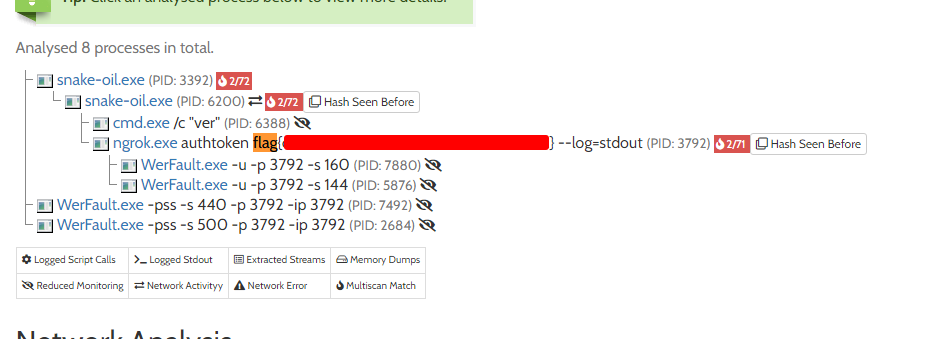
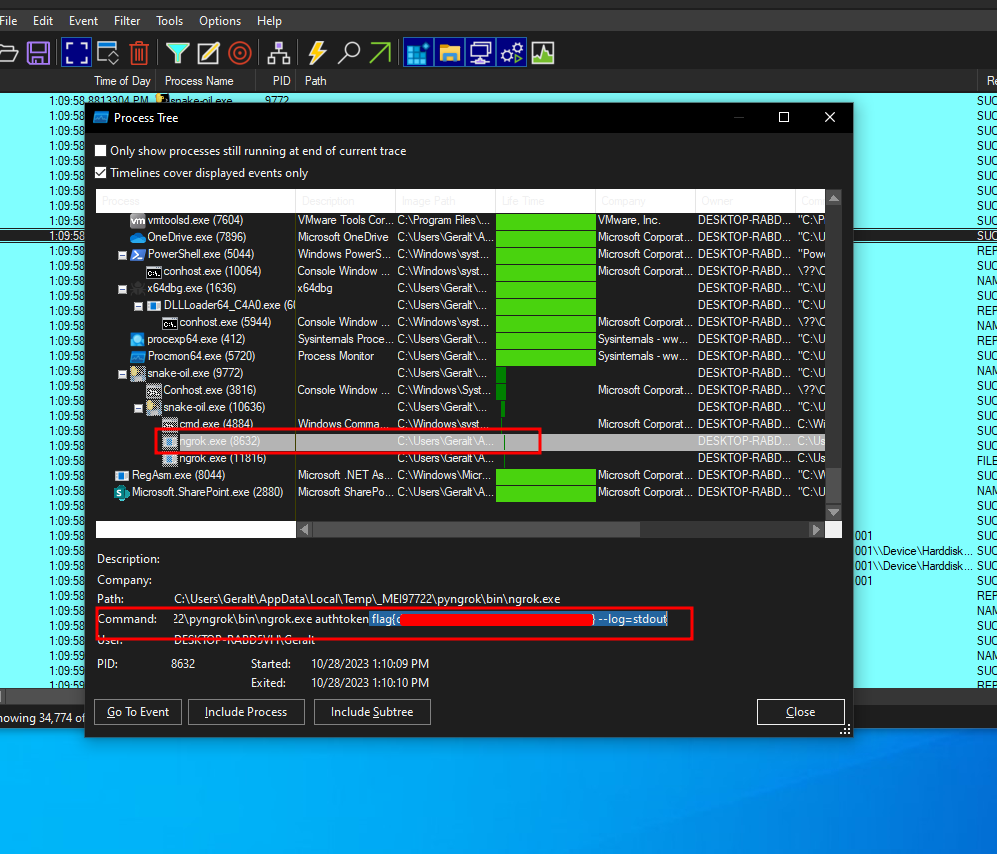
If we look at the process tree, we see ngrok server is one of the child processes, and we can find the flag in the command line section:
Method 2:
The next method, we used is static analysis in linux, the first tool we used is pyinstxtractor, which is a tool to extract the contents of a PyInstaller generated executable:
wget https://github.com/pyinstxtractor/pyinstxtractor-ng/releases/download/2023.10.12/pyinstxtractor-ng
./pyinstxtractor-ng snake-oil
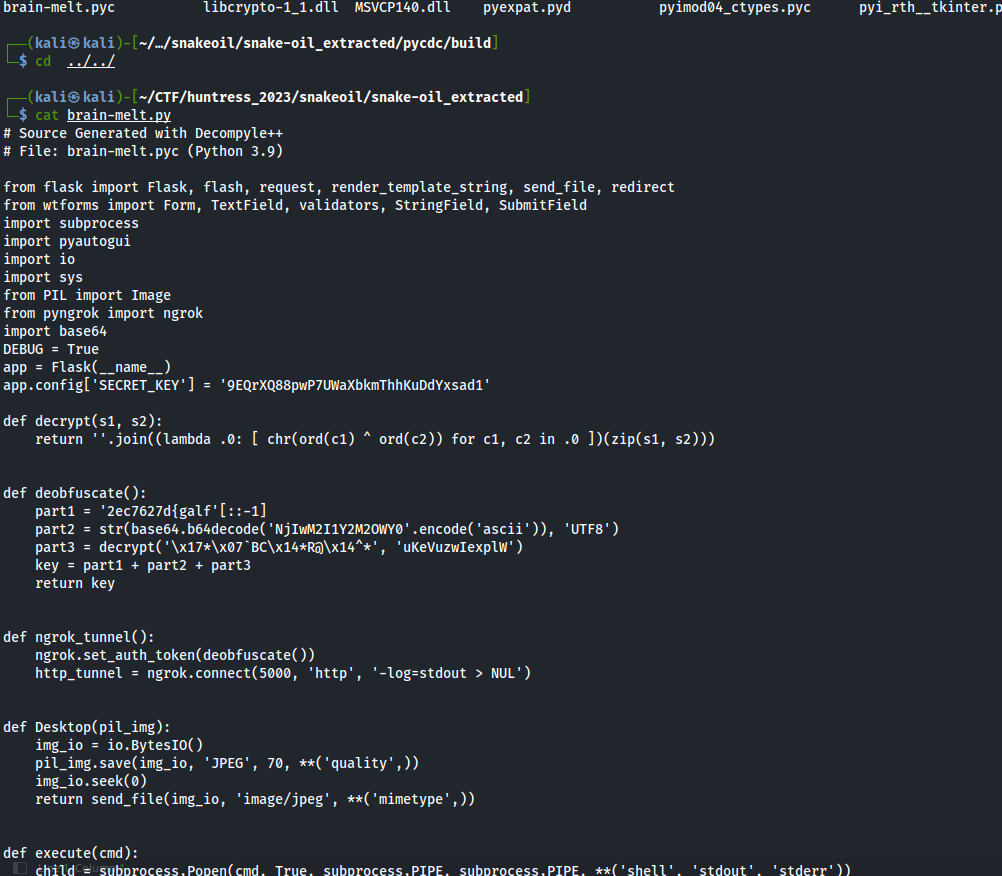
This gives us the contents of the PyInstaller binary, and we are interested in the brain-melt.pyc. We then used pycdc.
git clone https://github.com/zrax/pycdc.git
../pycdc ../../brain-melt.pyc > ../../brain-melt.py
This will give us a partially decompiled brain-melt.py:
Then, in our own python terminal, we can decrypt the flag!
#/usr/bin/env python3
import base64
def decrypt(s1, s2):
return ''.join((lambda x: [ chr(ord(c1) ^ ord(c2)) for c1, c2 in x ])(zip(s1, s2)))
def deobfuscate():
part1 = '2ec7627d{galf'[::-1]
part2 = str(base64.b64decode('NjIwM2I1Y2M2OWY0'.encode('ascii')), 'UTF8')
part3 = decrypt('\x17*\x07`BC\x14*R@\x14^*', 'uKeVuzwIexplW')
key = part1 + part2 + part3
return key
deobfuscate()

Method 3:
We uploaded the file to an online tool: hybrid-analysis